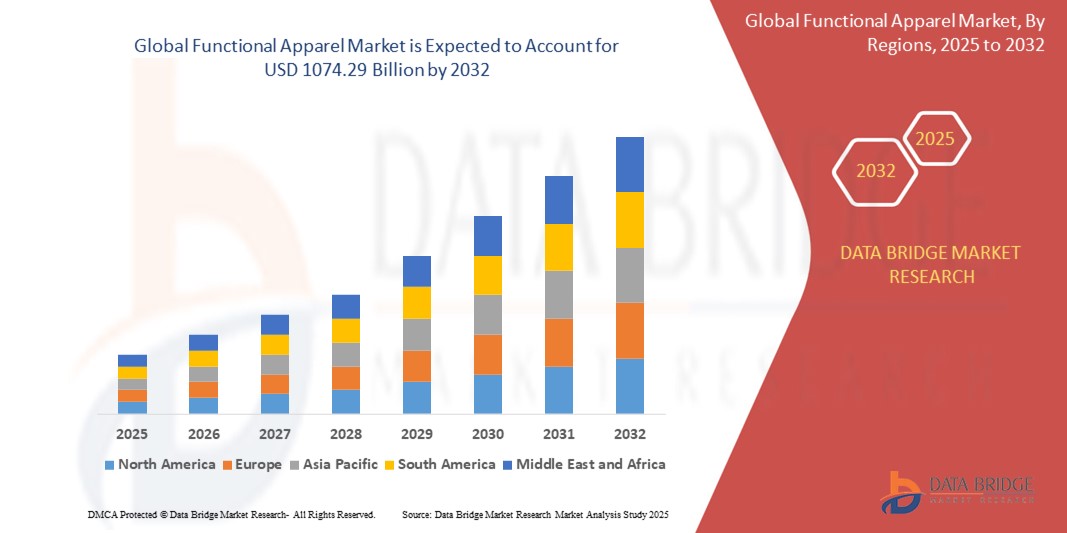
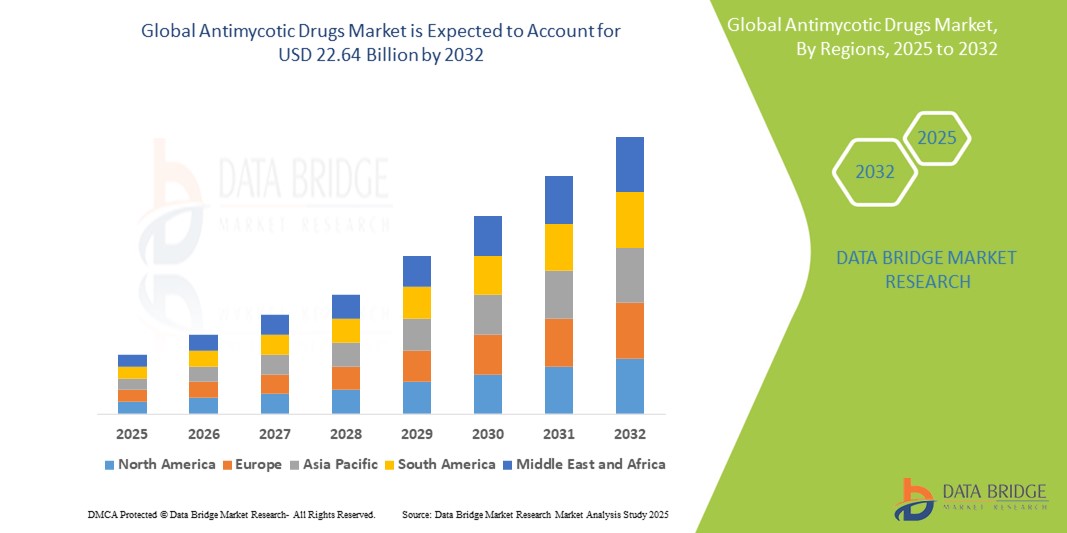
How to Update Android Version
How to Update Android Version Keeping your Android device updated is one of the most critical steps in ensuring optimal performance, security, and access to the latest features. Android updates include security patches, bug fixes, performance improvements, and sometimes major user interface overhauls. Whether you're using a flagship smartphone from Samsung, Google, or OnePlus, or a budget device f
How to Update Android Version
Keeping your Android device updated is one of the most critical steps in ensuring optimal performance, security, and access to the latest features. Android updates include security patches, bug fixes, performance improvements, and sometimes major user interface overhauls. Whether you're using a flagship smartphone from Samsung, Google, or OnePlus, or a budget device from Xiaomi or Realme, staying current with your Android version enhances your overall experience and protects your personal data from emerging threats.
Many users delay updates due to concerns about battery drain, app compatibility, or the fear of losing data. However, modern Android systems are designed to handle updates safely, with built-in safeguards to preserve your files and settings. This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step walkthrough on how to update your Android version, along with best practices, essential tools, real-world examples, and answers to frequently asked questions. By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to update your device efficiently and securely—no matter your technical background.
Step-by-Step Guide
Updating your Android version is a straightforward process, but the exact steps may vary slightly depending on your device manufacturer, model, and Android version currently installed. Below is a universal guide that applies to the vast majority of Android smartphones released in the last five years.
1. Check Your Current Android Version
Before initiating an update, it’s important to know which version of Android your device is currently running. This helps you determine whether an update is available and what changes you can expect.
To check your Android version:
- Open the Settings app.
- Scroll down and tap About phone (or About device on some brands).
- Look for Android version and Security patch level.
Make a note of these details. If your Android version is more than two years old or your security patch is outdated, an update is likely available.
2. Ensure Your Device Meets Update Requirements
Not all devices can receive every Android update. Manufacturers typically support flagship models with 3–4 years of updates, while budget devices may receive only one or two. Before proceeding, confirm your device is eligible:
- Check your manufacturer’s official support page (e.g., Samsung, Google Pixel, Xiaomi) for update timelines.
- Ensure your device has at least 50% battery or is connected to a charger.
- Connect to a stable Wi-Fi network. Updates can be several gigabytes in size and will consume mobile data if not on Wi-Fi.
- Free up at least 2–4 GB of internal storage. Temporary files during the update process require space.
3. Back Up Your Data (Recommended)
Although Android updates are designed to preserve your apps, photos, messages, and settings, unexpected issues can occur. A backup is a simple precaution that can save you from data loss.
To back up your data:
- Go to Settings > Google > Backup.
- Ensure Back up to Google Drive is turned on.
- Tap Back up now to initiate an immediate backup.
Additionally, manually copy important files (photos, videos, documents) to a computer or cloud service like Google Photos, Dropbox, or OneDrive. For media-heavy users, consider using a file manager app to transfer files via USB.
4. Connect to Wi-Fi and Charge Your Device
Android updates are large and require a stable internet connection. Using mobile data may result in interrupted downloads, extra charges, or failed installations.
Connect to a reliable Wi-Fi network:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi.
- Select your network and enter the password if needed.
Plug your device into a charger or ensure the battery is above 50%. Updating with low battery can cause the process to halt mid-installation, potentially corrupting the system.
5. Navigate to the Software Update Section
The location of the update menu varies slightly by manufacturer:
- Google Pixel: Settings > System > System updates
- Samsung: Settings > Software update > Download and install
- OnePlus: Settings > System > System updates
- Xiaomi / Redmi: Settings > About phone > System update
- OPPO / Realme: Settings > About phone > OTA update
- Motorola: Settings > System > Advanced > System updates
Tap on the update section. The system will automatically check for available updates. This may take 30 seconds to a few minutes.
6. Download and Install the Update
If an update is available, you’ll see a notification such as:
- "Android 14 is available"
- "Security update 2024-06-01"
- "System update: 2.5 GB"
Tap Download. The download progress will be displayed. Do not use your device heavily during this time, as it may slow the process.
Once downloaded, tap Install. Your device will reboot automatically. During installation:
- The screen may go black for several minutes.
- You may see a progress bar or Android logo with a spinning circle.
- Do not press any buttons or unplug the charger.
The entire process—from download to reboot—can take anywhere from 10 to 45 minutes, depending on your device and internet speed. Be patient.
7. Verify the Update
After your device restarts, confirm the update was successful:
- Go to Settings > About phone.
- Check Android version and Security patch level.
- Compare these to the version you saw before the update.
If the numbers have increased, the update was successful. You may also notice new features, redesigned icons, or improved performance.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with proper preparation, issues can arise. Here are common problems and how to resolve them:
Update Not Showing Up
If no update appears, try:
- Restarting your device and checking again.
- Manually checking for updates by tapping Check for updates in the software update menu.
- Ensuring your region and carrier settings are correct—some updates roll out regionally.
- Waiting a few days. Manufacturers deploy updates in waves, so your device may not be eligible yet.
Insufficient Storage
Clear cache and uninstall unused apps:
- Go to Settings > Storage.
- Tap Cached data and clear it.
- Review apps and remove those you no longer use.
- Move photos and videos to cloud storage.
Update Stuck or Fails
If the update freezes or fails:
- Wait 15–20 minutes. Sometimes the system is processing in the background.
- If it remains stuck, force restart by holding the Power button for 15–20 seconds until the device turns off, then turn it back on.
- If the device boots but the update didn’t install, return to the Software Update menu and try again.
- If the device enters a boot loop (repeats startup), you may need to perform a factory reset via recovery mode (see Section 5 for instructions).
Best Practices
Updating your Android version isn’t just about clicking a button—it’s a process that benefits from thoughtful preparation and ongoing maintenance. Following best practices ensures smoother updates, fewer errors, and long-term device health.
1. Prioritize Security Updates
Security patches are released monthly by Google and device manufacturers to fix vulnerabilities exploited by hackers. These updates often don’t change the Android version number but are critical for protecting your personal data.
Never ignore a security update. Even if you’re not interested in new features, patching known exploits prevents malware, phishing, and unauthorized access.
2. Avoid Third-Party Update Tools
Many websites and apps claim to “boost your Android version” or “unlock Android 15.” These are often scams, malware carriers, or outdated tools that can brick your device.
Only use official update channels:
- Device manufacturer’s update system
- Google’s OTA (Over-the-Air) updates
- Android Debug Bridge (ADB) for advanced users (see Tools section)
Never sideload update files from unknown sources unless you are experienced and understand the risks.
3. Update During Off-Peak Hours
Network congestion can slow download speeds. If possible, initiate updates late at night or early in the morning when fewer people are using the internet. This ensures faster downloads and reduces the chance of interruptions.
4. Monitor Battery Health
Older batteries may not handle the power demands of a system update. If your device’s battery health is below 80%, consider replacing it before updating. A failing battery can cause the update to fail mid-process.
To check battery health on supported devices:
- Go to Settings > Battery > Battery health (available on Pixel, Samsung, and some OnePlus devices).
- If unavailable, use third-party apps like AccuBattery to estimate health.
5. Keep Apps Updated Too
Android updates often include changes to APIs and system libraries. Outdated apps may crash or behave erratically after a system update.
Before updating Android:
- Open the Google Play Store.
- Tap your profile icon > Manage apps & device.
- Tap Updates available and update all apps.
This minimizes compatibility issues after the Android update completes.
6. Don’t Update on Public Wi-Fi
Public networks are often unsecured and can be targeted by attackers. While downloading an update, your device communicates with Google’s servers. On an insecure network, this communication could be intercepted.
Always use a trusted, password-protected home or work Wi-Fi network for updates.
7. Read Release Notes
Manufacturers often publish release notes for major updates. These documents detail new features, known issues, and device-specific changes.
For example:
- Google Pixel: source.android.com
- Samsung: samsung.com/support/updates
Reading release notes helps you understand what to expect and whether the update resolves issues you’ve experienced.
Tools and Resources
While most users rely on built-in OTA updates, advanced users and tech enthusiasts may benefit from additional tools and resources to manage Android updates more effectively.
1. Android Debug Bridge (ADB) and Fastboot
ADB is a command-line tool that allows you to communicate with your Android device from a computer. It’s useful for manually installing system updates, especially when OTA updates fail or are unavailable.
To use ADB:
- Download the Android Platform Tools from Google’s official site.
- Extract the ZIP file to a folder on your computer (e.g., C:\platform-tools).
- Enable Developer Options on your phone: Go to Settings > About phone > Software information, then tap Build number seven times.
- In Developer Options, enable USB debugging.
- Connect your phone via USB.
- Open Command Prompt or Terminal, navigate to the platform-tools folder, and type:
adb devicesto confirm connection. - Use
adb sideload filename.zipto manually install a system update file.
⚠️ Warning: Improper use of ADB can brick your device. Only proceed if you have downloaded the correct update file for your exact model.
2. Manufacturer-Specific Update Tools
Some manufacturers provide desktop software for updating firmware:
- Samsung Smart Switch: Allows firmware updates via PC and data transfer.
- Huawei HiSuite: Used for firmware updates and backup on Huawei devices.
- OPPO / Realme USB Driver + Update Tool: Available on official support sites.
These tools are especially helpful if your device is stuck on an old version and won’t receive OTA updates.
3. Custom ROMs (Advanced Users Only)
For devices no longer supported by manufacturers, custom ROMs like LineageOS, Pixel Experience, or crDroid offer updated Android versions with enhanced features.
Benefits:
- Access to newer Android versions even on discontinued devices
- Removal of bloatware
- Improved privacy controls
Drawbacks:
- Voiding warranty
- Loss of official security updates
- Risk of instability or hardware incompatibility
Before installing a custom ROM:
- Research compatibility on XDA Developers.
- Backup all data.
- Unlock bootloader (this erases all data).
- Install a custom recovery like TWRP.
Custom ROMs are not recommended for casual users but are a powerful option for extending device life.
4. Official Support Websites
Always refer to your device manufacturer’s official support pages for accurate update information:
- Google Pixel: support.google.com/pixelphone
- Samsung: samsung.com/support/updates
- OnePlus: oneplus.com/support
- Xiaomi: mi.com/global/miuidownload
- Motorola: motorola.com/support-updates
These sites list supported devices, update schedules, and manual firmware download links.
5. Android Version Compatibility Chart
Here’s a quick reference for Android versions and their support status as of 2024:
| Android Version | Release Year | Current Support Status |
|---|---|---|
| Android 14 | 2023 | Active (Latest) |
| Android 13 | 2022 | Active (Security patches) |
| Android 12 | 2021 | End of Life (No longer receiving updates) |
| Android 11 | 2020 | End of Life |
| Android 10 | 2019 | End of Life |
Devices running Android 12 or older are at increased security risk. Plan to upgrade your device if it no longer receives updates.
Real Examples
Real-world scenarios help illustrate how Android updates work in practice. Below are three detailed examples from different device categories.
Example 1: Google Pixel 6 Pro – Seamless OTA Update
John owns a Google Pixel 6 Pro purchased in 2022. He had been running Android 13 with a security patch from January 2024. On June 5, 2024, he received a notification: “Android 14 is ready to install.”
John followed these steps:
- Connected to home Wi-Fi.
- Plugged in his charger.
- Backed up photos to Google Photos.
- Tapped “Download and Install.”
- Waited 22 minutes while the device rebooted.
After rebooting, his device showed Android 14, security patch June 2024. He noticed:
- New lock screen customization options
- Improved battery life
- Faster app launches
John’s experience was typical of flagship Pixel devices—smooth, fast, and fully supported.
Example 2: Samsung Galaxy A14 – Delayed Update
Sarah bought a Samsung Galaxy A14 in early 2023. It shipped with Android 13. By mid-2024, she noticed other users on forums had received Android 14, but her device showed “Your software is up to date.”
She researched and found that Samsung’s budget devices typically receive two major OS updates. The A14 was eligible for Android 14, but the rollout was delayed in her region (Southeast Asia).
Sarah waited three more weeks. On July 18, 2024, the update appeared. She followed the same steps as John and successfully upgraded.
Her takeaway: Budget devices may have delayed updates. Patience and checking official forums are key.
Example 3: Xiaomi Redmi Note 10 – Manual Update via Mi Account
David owned a Xiaomi Redmi Note 10 running Android 11. He hadn’t received any major updates since 2022. He was concerned about security.
He visited Xiaomi’s official update page and found a manual update file for Android 12 (MIUI 14) for his exact model (M2101K9AG).
He:
- Downloaded the update ZIP file.
- Transferred it to his phone’s internal storage.
- Went to Settings > About phone > System update > Manual update.
- Selected the file and tapped Install.
The device rebooted and successfully upgraded to Android 12. David was able to install security patches afterward.
This example shows that even unsupported devices can sometimes be updated manually using official firmware files.
FAQs
Can I update my Android version manually without Wi-Fi?
You can use mobile data, but it’s not recommended. Android updates are large (often 2–4 GB) and can consume your data plan quickly. If you must use mobile data, ensure you have sufficient allowance and disable background data usage during the download.
Will updating Android delete my apps and data?
No, official OTA updates are designed to preserve your apps, photos, messages, and settings. However, a failed update or manual flashing (via ADB or custom ROM) may erase data. Always back up before updating.
Why does my phone say “Your software is up to date” but others have a newer version?
Manufacturers roll out updates in phases. Your device may be in a later wave. Regional differences, carrier restrictions, or hardware compatibility can also delay updates. Wait a few days or check your manufacturer’s official update schedule.
Can I downgrade my Android version after updating?
Officially, no. Downgrading is not supported and can cause system instability or security issues. If you’re unhappy with an update, wait for a patch or consider a factory reset. Advanced users may flash older firmware via ADB, but this voids warranty and carries risks.
How often should I update my Android device?
Check for updates monthly. Security patches are released monthly; major OS updates (e.g., Android 13 → 14) typically come once a year. Install updates as soon as they’re available.
What if my device is no longer receiving updates?
If your device is over 4–5 years old, it may no longer receive updates. Consider upgrading to a newer model. In the meantime, avoid downloading apps from unknown sources, use a reputable antivirus app, and disable unused permissions to minimize risks.
Does updating Android improve battery life?
Often, yes. Newer Android versions include power-saving optimizations, better background app management, and improved hardware-software coordination. However, some users report temporary battery drain after a major update due to system reindexing—this usually resolves within a few days.
Is it safe to update an older Android device?
If your device is still officially supported, yes. If it’s no longer receiving updates, updating to the last available version is still beneficial. Avoid installing unofficial or custom updates unless you fully understand the risks.
Can I update Android on a tablet?
Yes. The process is identical to smartphones. Go to Settings > System > Software update. Tablets from Samsung, Google, and Apple (iPadOS is separate) receive updates similarly.
What happens if I don’t update my Android device?
Your device becomes vulnerable to security exploits. Apps may stop working due to API changes. You’ll miss out on performance improvements, new features, and accessibility enhancements. Over time, your device will become slower and less secure.
Conclusion
Updating your Android version is not just a technical task—it’s a vital part of digital hygiene. From enhanced security and improved performance to access to cutting-edge features, staying current ensures your device remains reliable, efficient, and protected against evolving threats.
This guide has walked you through the entire process: from checking your current version to troubleshooting failed updates, and from using official tools to understanding real-world scenarios. Whether you’re a casual user or a tech-savvy individual, the principles remain the same: prepare, update, verify, and maintain.
Remember: Never ignore security patches. Avoid third-party tools. Back up your data. And always use official channels. These simple habits can extend the life of your device and safeguard your digital life.
As Android continues to evolve, so should your approach to updates. By following the steps outlined here, you’re not just keeping your phone current—you’re taking control of your digital experience. Update confidently, update regularly, and enjoy the full potential of your Android device.